Describe the Action of Different Types of Chemical Mutagens
Some other chemical mutagens interfere with correct DNA replication by inserting themselves into the DNA distorting the double helix. Describe the action of difference types of chemical mutagens.

Where Do Mutations Come From Short Explainer Science Facts Reactive Oxygen Species Learning Centers
Write below the broader molecular definition in use today.

. Tests for heritable mutagenicityin Drosophila and experimental mammals have. Carcinogens that do not directly damage DNA include substances that accelerate cell division thereby leaving less opportunity for cell to repair induced mutations or errors in replication. Various types of chemical mutagens interact directly with DNA either by acting as nucleoside analogs or by modifying nucleotide bases.
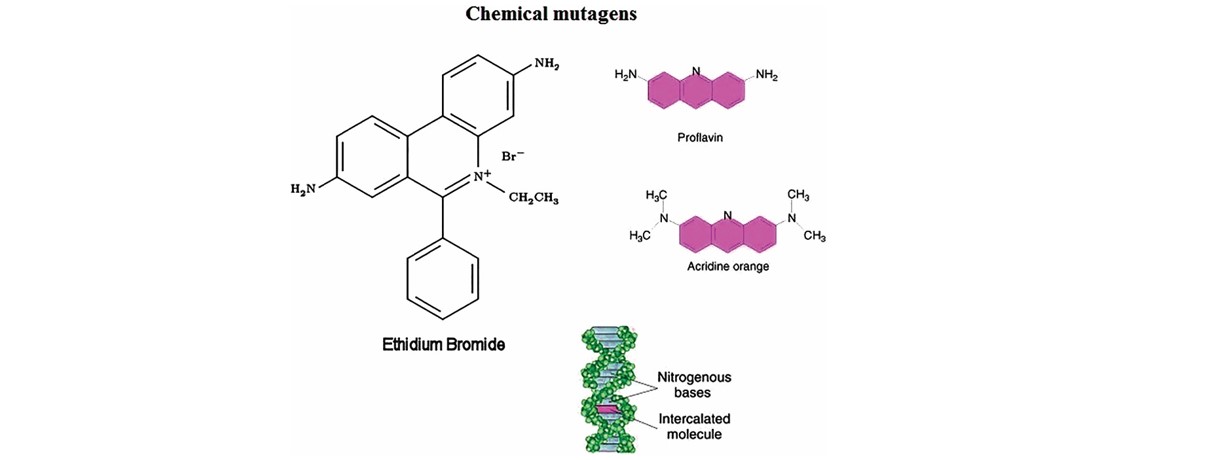
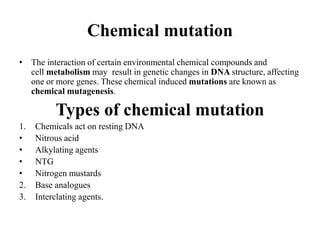
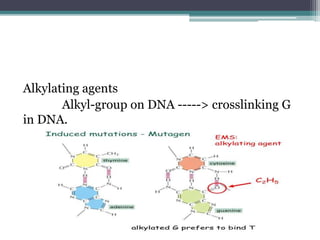
This is the most powerful group of mutagens. At the molecular level the mutagens create different gene mutations results in loss of function altered function or non-functional protein. Base analogs 5-bromouracil T or rarely C hydroxylating agent add OH-group to C alkylating agent such as EMS ethylmethane sulfonate deaminating agent such as nitrous acid intercalating agent such as Acridine Orange.
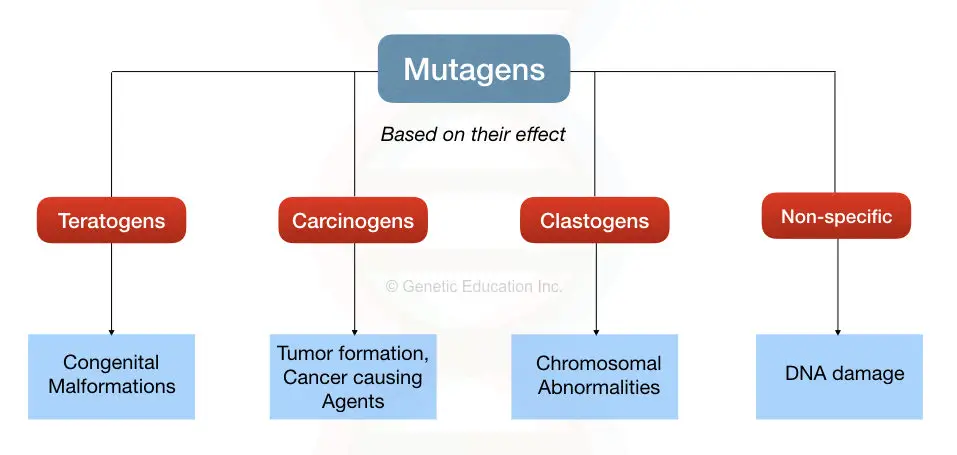
Null mutation makes the gene turned on at all time constitutively c-. Mutagenic treatment of seeds is the most convenient and therefore the standard method in seed propagated crops. Carcinogens that act as mutagens may be biological physical or chemical in nature although the term is most often used in relation to chemical substances.
Describe the action of different types of chemical mutagens. Mutagen treatment greatly increases the mutation rate Exposure to X-ray UV light Chemical treatment. Various types of chemical mutagens interact directly with DNA either by.
All mutagens have characteristic mutational. Chemicals called nucleoside analog s are structurally similar to normal nucleotide bases and can be incorporated into DNA during replication Figure 1120. Fill the Table with mutagenic agents and provide their type physical chemical biological and their classification based on their effect teratogenic carcinogenic clastogenic or non-specific together with their modes of action.
Mutagen Type of Mutagen Classification based on effect Action 2-aminopurine Acridine orange Proflavine. 1 Alkylating agents 2 Base analogues 3 Acridine dyes and 4 Others Table 253. Constitutive on in the absence of signal b-.
These base analogs induce mutations because they often. A mutagen is a mutation-causing agent be it chemical or physical which results in an increased. It is a chemical mutagen and it produce point mutation in plant genome by producing metabolites and produced protein in mutant plants which is having different function than in normal plants.
It can also be achieved experimentally using laboratory procedures. Null mutation makes insensitive to signal Negative action-represses next step. In genetics a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that permanently changes genetic material usually DNA in an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level.
As many mutations can cause cancer such mutagens are therefore carcinogens although not all necessarily are. Some of the chemical mutagens and mutagenesis are given in Table 93 and described below. Singer and Kusmierek 1982 have published an excellent review on chemical mutagenesis.
Ethylene oxide EtO and ethylene dibro-mide EDB. In terms of function DNA glycosylases are either monofunctional with only a glycosylase activity such as the uracil glycosylases N-methylpurine DNA Glycosylase. A base analogue is a chemical compound.
Physical mutagens include electromagnetic radiation such as gamma rays X rays and UV light and particle radiation such as fast and thermal neutrons beta and alpha particles. It may occur spontaneously in nature or as a result of exposure to mutagens. Positive action-stimulate next step.
Describe the action of different types of chemical mutagens Base analogs are chemicals that are that are similar to normal DNA bases but pair incorrectly during DNA replication. What is a gene. In Oklahoma crop production 11 different herbicide modes of action are commonly used and each is unique in the way it controls susceptible plants.
Describe two important ways in which bacterial and eukaryotic gene expression differ. Chemicals called nucleoside analogs are structurally similar to normal nucleotide bases and can be incorporated into DNA during replication Figure PageIndex3. Mutagenesis mjuːtəˈdʒɛnɪsɪs is a process by which the genetic information of an organism is changed by the production of a mutation.
Concept 176 Although gene expression differs among the domains of life the concept of a gene is universal. Various types of chemical mutagens interact directly with DNA either by acting as nucleoside analogs or by modifying nucleotide bases. Mutant plants which are produced by using sodium azide have capacity to survive in adverse conditions greater stress tolerance increase shelf life improved yield lesser.
In this article we will discuss about the chemical and physical types of mutagens. Mutagens and their actions Chan Ho Yin Aurora 02690763 Chen Yiwei Echo 01790443 Co NgaiNa Chloe 02715283 Lam Kit MingGermaine02770293 Mutation Spontaneous Mutation Induced Mutation Mutagen Chemical Mutagens. Up to 24 cash back 74.
A brief description of some commonly used chemicals of these groups is presented below. Krokan and Bjoras 2013. Never turned on even in the presence of the signal b-c- c-.
115 OSHA has included thoroughreviews of mu- tagenicity data in notices of regulatory actions for two of the best-publicized chemical hazards of the 1980s. Some herbicide modes of action comprise several chemical families that vary slightly in their chemical composition but control susceptible plants in the same way and cause similar injury symptoms. At least 11 different DNA glycosylases can recognize and excise a damaged base from undistorted helices as well as ones flipped out from the major groove Huffman et al 2005.
Most chemical mutagens are alkylating agents and azides. There are three main types of mutagens classifying by their. The chemical mutagens can be divided into four groups viz.
It used to be simply stated that one gene codes for one polypeptide. That definition has now been modified. It also alters the codon deletes bases alters bases breaks hydrogen bonds or phosphodiester bonds and changes gene expression.
Learn About Chemical Mutagen Chegg Com

Mutagen Definition Types And Effect Genetic Abnormalities Gene Expression Chromosomal Abnormalities
Mutagen Definition Types And Effect

Chemical Mutagen Agents Examples How Chemical Mutagens Damage Dna Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Mutagen Definition Types And Examples I Researchtweet

Methods To Identify Mutagens Download Scientific Diagram

Mutagenesis And Mutagens Online Biology Notes

Mutagens Physical Chemical And Biological Mutagenic Agents Infinity Learn

Examples Of Commonly Used Physical Mutagens Download Table

Physical And Chemical Mutagen Copy

Types Of Mutagens Chemical And Physical Genetics
Chemical Aspects Of Mutagens 1 1

Chemical Mutagen An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Mutagen Definition Types And Examples I Researchtweet

Types Of Mutagens Phycial Chemical Base Analog 5 Bromo Uracil Biological Youtube

1 Different Kinds Of Physical And Chemical Mutagens That Are Mostly Download Scientific Diagram


Comments
Post a Comment